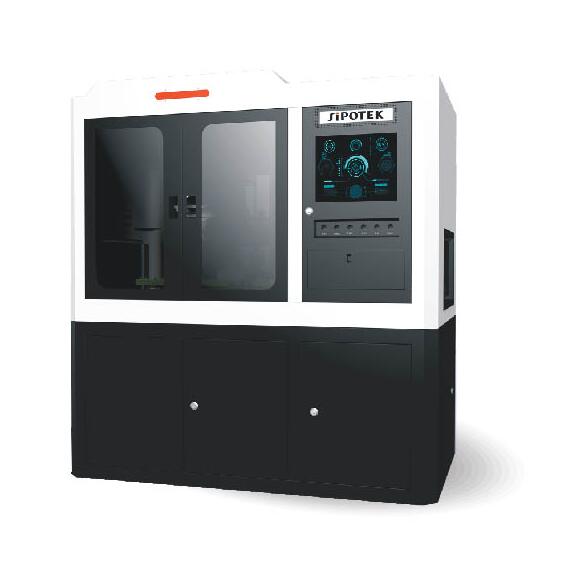
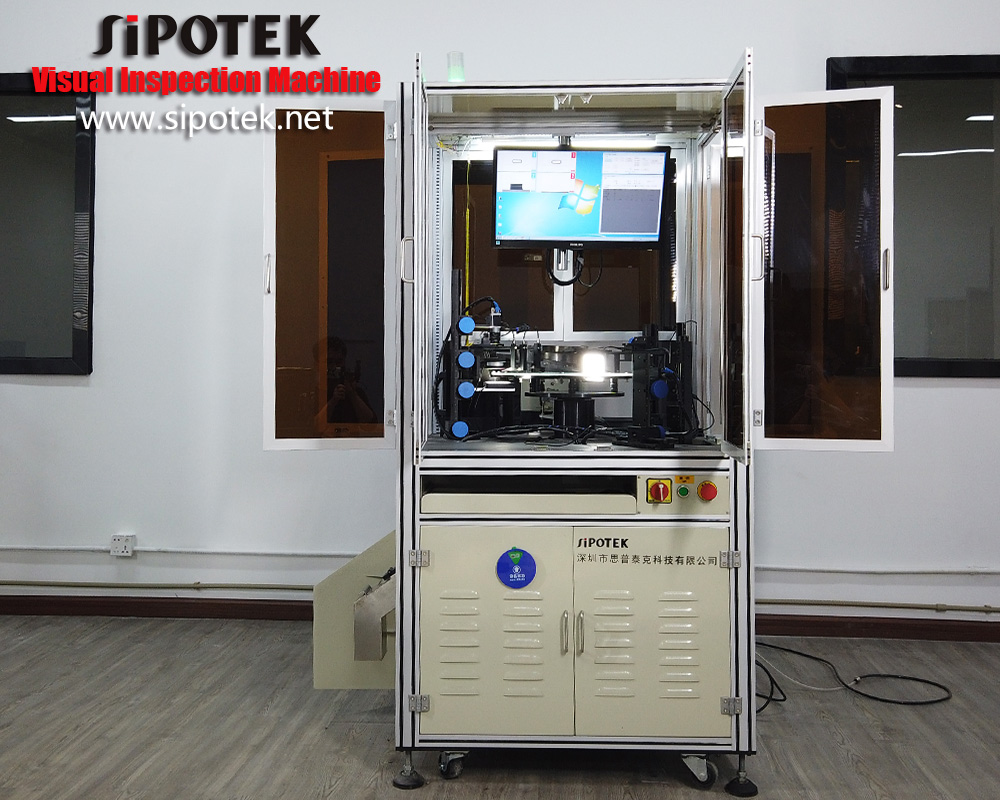
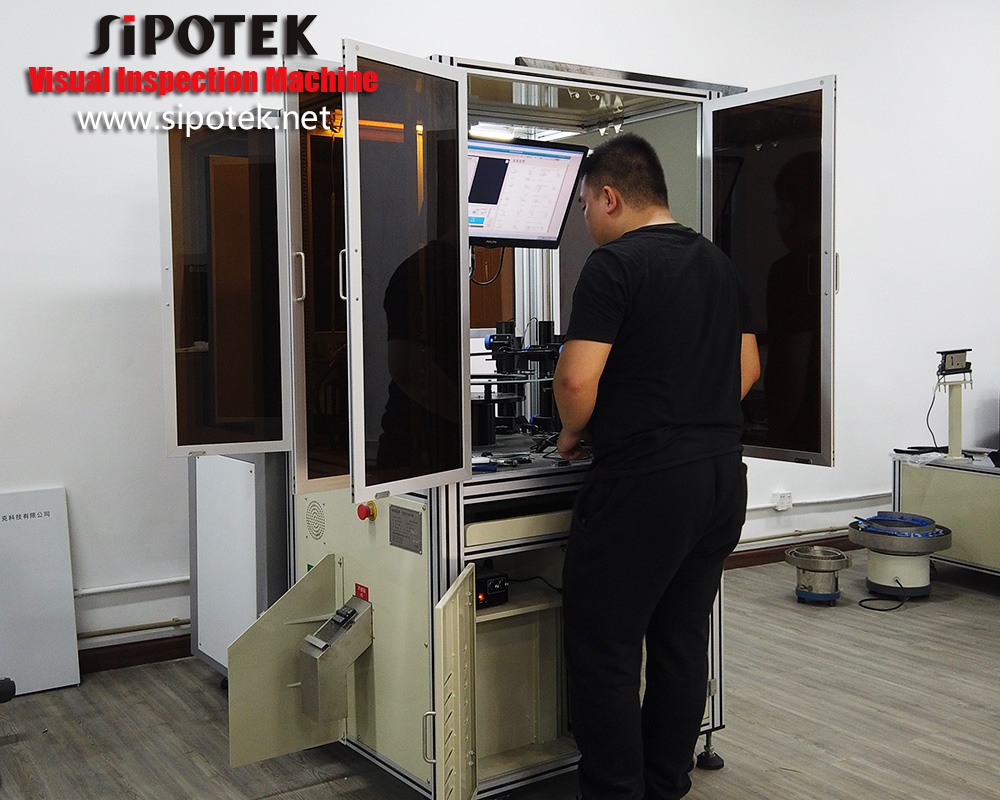
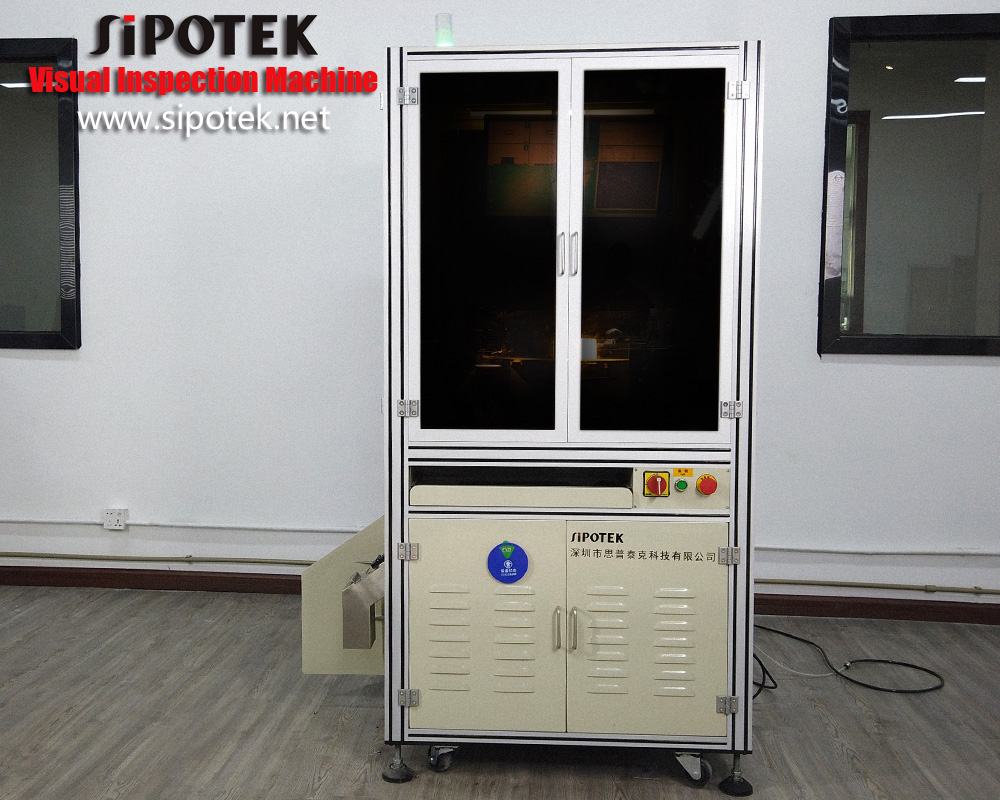
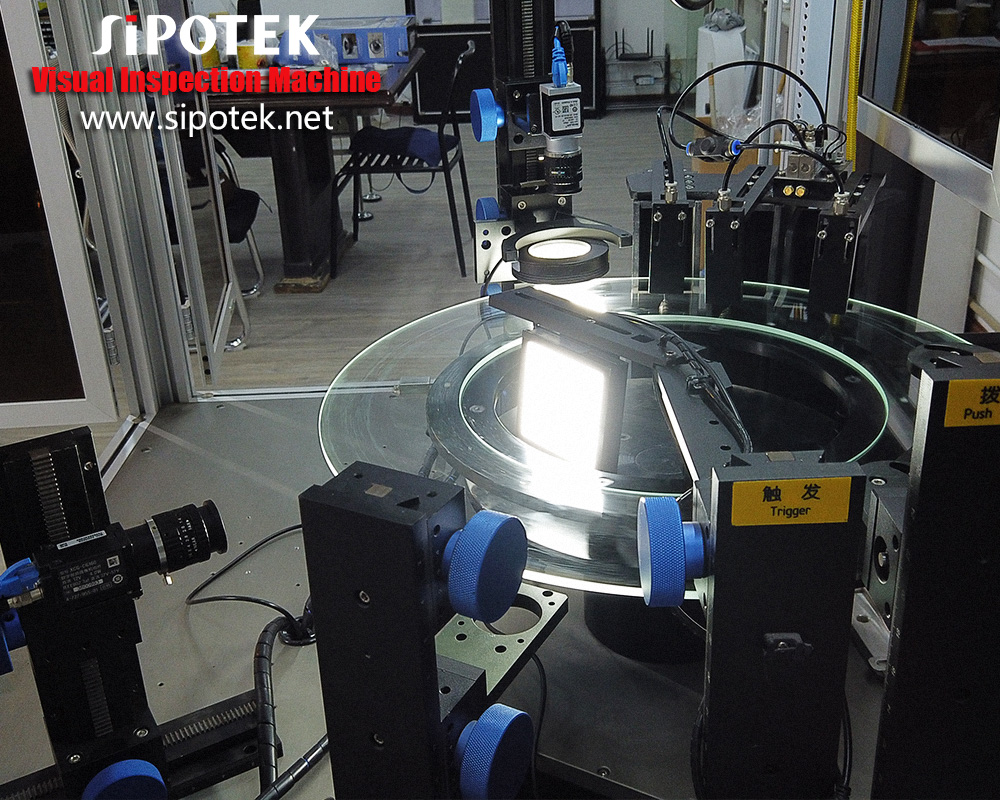
We usually use a 2D optical sorting inspection machine to detect the o-rings. They are very small size products. For offline inspection, we can feed a number of rings into the vibration feeder, the mechanism will hold them with motion and make them ready to stand in sequence to a conveyor belt. The rings are one by one carried to a rotary glass plate, which we called the inspection section. The cameras are standby to capture images of each ring. After the image processing system finish the data transmission, the machine will take action to the rings. OK rings will be carried to a delicate output while NG rings to another output.

To understand how the defects can be inspected, knowing more about the kind of defects is also helpful.
Tony Rogers explained some of the molding defects that can occur in a part during injecting molding. Include ten common defects.
1. Flow lines. They are streaks, patterns, or lines – commonly off-toned in color – that show up on the prototype part as a consequence of the physical path and cooling profile of the molten plastic as it flows via an entry section called a “gate”. It then flows through the tool cavity and cools.
2. Sink Marks. Sink marks are often caused when the cooling time or the cooling mechanism is insufficient for the plastic to fully coll and cure while in the mold. They can also be caused by inadequate pressure in the cavity, or by an excessive temperature at the gate. All else being equal, thick sections of the injection molded part take longer to cool than thin ones and so are more likely to be where sink marks are located.
3. Vacuum voids. Vacuum voids are pockets of air trapped within or close to the surface of an injection molded prototype. They are often caused by uneven solidification between the surface and the inner sections of the prototype.
4. Surface Delamination. Surface delamination is a condition where thin surface layers appear on the part due to a contaminant material. These layers appear like coatings and can usually be peeled off. Seems like burrs. Foreign materials that find their way into the molten plastic separate from the finished product because the contaminant and the plastic cannot bond. The fact that they cannot bond not only has an affect on the appearance of the prototype, but also on its strength. The contaminant acts as a localized fault trapped within the plastic.
5. Weld lines. They are more like a plane than a line that appears in a part where molten plastics meet each other as they flow from two different parts of the mold.
6. Short shot. It can be described as a situation where a molding shot falls short. This means that the molten plastic for some reason does not fully occupy the mold cavity or cavities, resulting in a portion where there is no plastic. The finished product becomes incomplete. Sometimes we call it missing materials.
7. Warping is the deformation that occurs when there is uneven shrinkage in the different parts of the molded component. The result is a twisted, uneven, or bent shape where one was not intended. It is usually caused by non-uniform cooling of the mold materials. Different cooling rates in different parts of the mold cause the plastic to cool differently and thus create internal stresses. These stresses, when released, lead to warping.
8. Burn Marks. Burn marks are caused either by the degradation of the plastic material due to excessive heating or by injection speeds that are too fast. Burn marks can also be caused by the overheating of trapped air, which etches the surface of the molded part.
9. Jetting. Jetting refers to a situation where molten plastic fails to stick to the mold surface due to the speed of injection. Being fluid, the molten plastic solidifies in a state that shows the wavy folds of the jet stream on the surface of the injection molded part. It occurs when the melt temperature is too low and the viscosity of the molten plastic becomes too high, thereby increasing the resistance of its flow through the mold.
10. Flash is a molding defect that occurs when some molten plastic escapes from the mold cavity. Typical route for escape are through the parting line or ejector pin locations. This extrusion cools and remains attached to the finished product.

About Shenzhen Sipotek Technology Co., Ltd
Started in 2002, Sipotek Technology is located in Shenzhen in China. The company designs and manufactures visual inspection systems with its avant-garde R&D department and a great experience in artificial vision technologies. Sipotek is a professional machine vision inspection system manufacturer from china.The Sipotek Technology staff supports customers 360 degrees automatd optical inspection(AOI), from listening to their requests to the development of ambitious machines for quality control.
For Inquiries:
Contact Person: James Yuan
Company: Shenzhen Sipotek Technology Co., Ltd
Tel: +86 18666216027
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.topvision.net














